What Is Project Risk Analysis?
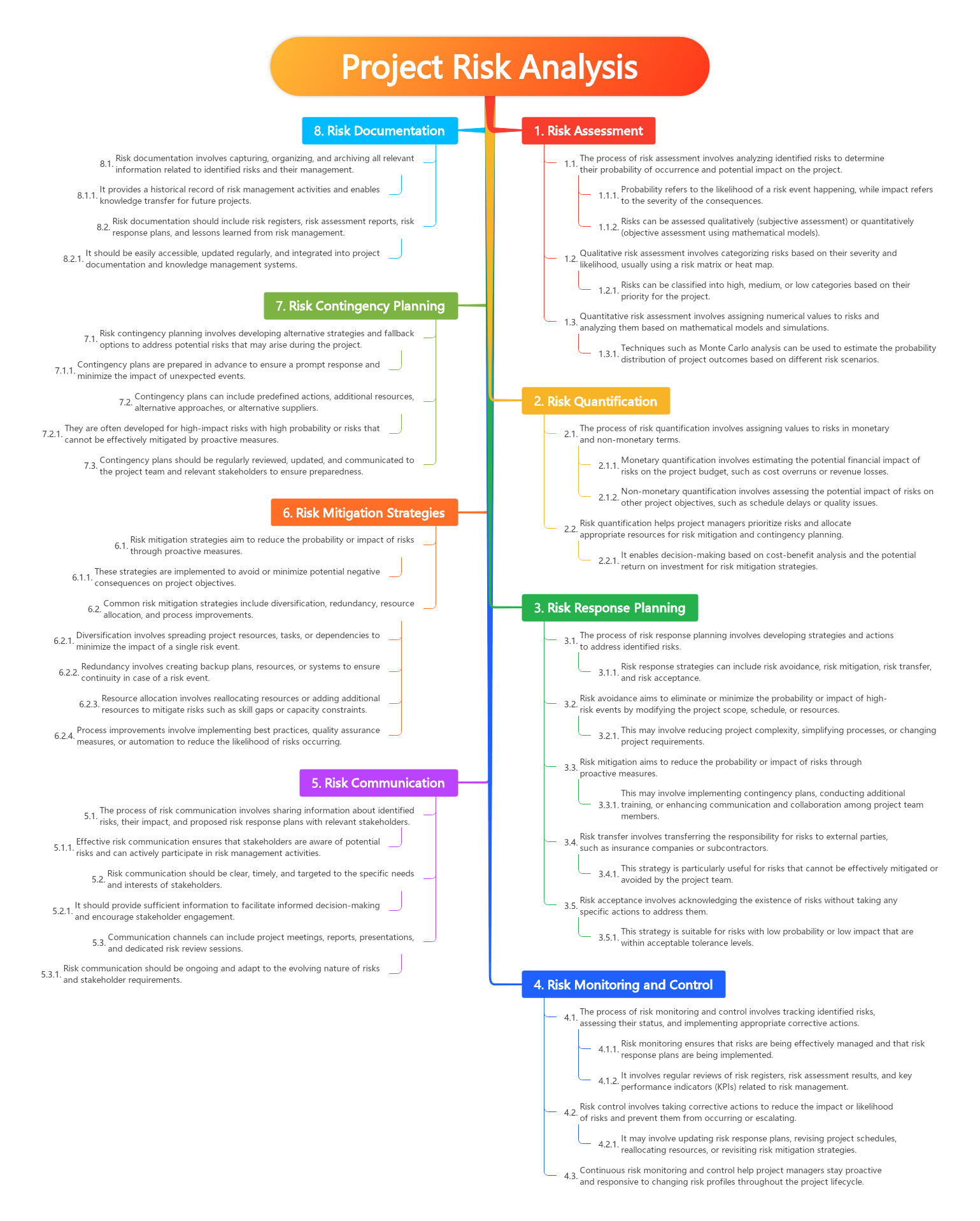
- Risk Assessment
- The process of risk assessment involves analyzing identified risks to determine their probability of occurrence and potential impact on the project.
- Probability refers to the likelihood of a risk event happening, while impact refers to the severity of the consequences.
- Risks can be assessed qualitatively (subjective assessment) or quantitatively (objective assessment using mathematical models).
- Qualitative risk assessment involves categorizing risks based on their severity and likelihood, usually using a risk matrix or heat map.
- Risks can be classified into high, medium, or low categories based on their priority for the project.
- Quantitative risk assessment involves assigning numerical values to risks and analyzing them based on mathematical models and simulations.
- Techniques such as Monte Carlo analysis can be used to estimate the probability distribution of project outcomes based on different risk scenarios.
- Risk Quantification
-
- The process of risk quantification involves assigning values to risks in monetary and non-monetary terms.
- Monetary quantification involves estimating the potential financial impact of risks on the project budget, such as cost overruns or revenue losses.
- Non-monetary quantification involves assessing the potential impact of risks on other project objectives, such as schedule delays or quality issues.
- Risk quantification helps project managers prioritize risks and allocate appropriate resources for risk mitigation and contingency planning.
- It enables decision-making based on cost-benefit analysis and the potential return on investment for risk mitigation strategies.
- Risk Response Planning
- The process of risk response planning involves developing strategies and actions to address identified risks.
- Risk response strategies can include risk avoidance, risk mitigation, risk transfer, and risk acceptance.
- Risk avoidance aims to eliminate or minimize the probability or impact of high-risk events by modifying the project scope, schedule, or resources.
- This may involve reducing project complexity, simplifying processes, or changing project requirements.
- Risk mitigation aims to reduce the probability or impact of risks through proactive measures.
- This may involve implementing contingency plans, conducting additional training, or enhancing communication and collaboration among project team members.
- Risk transfer involves transferring the responsibility for risks to external parties, such as insurance companies or subcontractors.
- This strategy is particularly useful for risks that cannot be effectively mitigated or avoided by the project team.
- Risk acceptance involves acknowledging the existence of risks without taking any specific actions to address them.
- This strategy is suitable for risks with low probability or low impact that are within acceptable tolerance levels
- Risk Monitoring and Control
- The process of risk monitoring and control involves tracking identified risks, assessing their status, and implementing appropriate corrective actions.
- Risk monitoring ensures that risks are being effectively managed and that risk response plans are being implemented.
- It involves regular reviews of risk registers, risk assessment results, and key performance indicators (KPIs) related to risk management.
- Risk control involves taking corrective actions to reduce the impact or likelihood of risks and prevent them from occurring or escalating.
- It may involve updating risk response plans, revising project schedules, reallocating resources, or revisiting risk mitigation strategies.
- Continuous risk monitoring and control help project managers stay proactive and responsive to changing risk profiles throughout the project lifecycle.
- Risk Communication
- The process of risk communication involves sharing information about identified risks, their impact, and proposed risk response plans with relevant stakeholders.
- Effective risk communication ensures that stakeholders are aware of potential risks and can actively participate in risk management activities.
- Risk communication should be clear, timely, and targeted to the specific needs and interests of stakeholders.
- It should provide sufficient information to facilitate informed decision-making and encourage stakeholder engagement.
- Communication channels can include project meetings, reports, presentations, and dedicated risk review sessions.
- Risk communication should be ongoing and adapt to the evolving nature of risks and stakeholder requirements
- Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Risk mitigation strategies aim to reduce the probability or impact of risks through proactive measures.
- These strategies are implemented to avoid or minimize potential negative consequences on project objectives.
- Common risk mitigation strategies include diversification, redundancy, resource allocation, and process improvements.
- Diversification involves spreading project resources, tasks, or dependencies to minimize the impact of a single risk event.
- Redundancy involves creating backup plans, resources, or systems to ensure continuity in case of a risk event.
- Resource allocation involves reallocating resources or adding additional resources to mitigate risks such as skill gaps or capacity constraints.
- Process improvements involve implementing best practices, quality assurance measures, or automation to reduce the likelihood of risks occurring.
- Risk Contingency Planning
- Risk contingency planning involves developing alternative strategies and fallback options to address potential risks that may arise during the project.
- Contingency plans are prepared in advance to ensure a prompt response and minimize the impact of unexpected events.
- Contingency plans can include predefined actions, additional resources, alternative approaches, or alternative suppliers.
- They are often developed for high-impact risks with high probability or risks that cannot be effectively mitigated by proactive measures.
- Contingency plans should be regularly reviewed, updated, and communicated to the project team and relevant stakeholders to ensure preparedness.
- Risk Documentation
- Risk documentation involves capturing, organizing, and archiving all relevant information related to identified risks and their management.
- It provides a historical record of risk management activities and enables knowledge transfer for future projects.
- Risk documentation should include risk registers, risk assessment reports, risk response plans, and lessons learned from risk management.
- It should be easily accessible, updated regularly, and integrated into project documentation and knowledge management systems.