Professionals Job Profiles:
Unlock the Doors to Digital Domains: Find Your Niche in the IT Landscape
The top most 50 IT job profiles’ common areas clarifies their roles and shows how they contribute across IT sectors. This comprehensive categorization highlights software and application development, cybersecurity, data science, and cloud computing opportunities. Grouping these positions into domains helps aspiring IT professionals navigate their career paths by revealing the specialised skills and expertise needed in each field. This organised approach highlights the diversity and dynamism of the IT sector, showing digital adventurers a world of opportunities.
Career Progression:
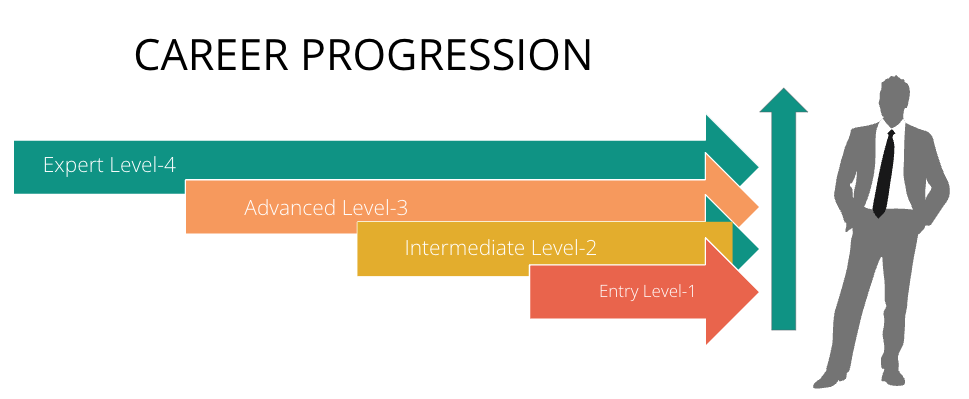
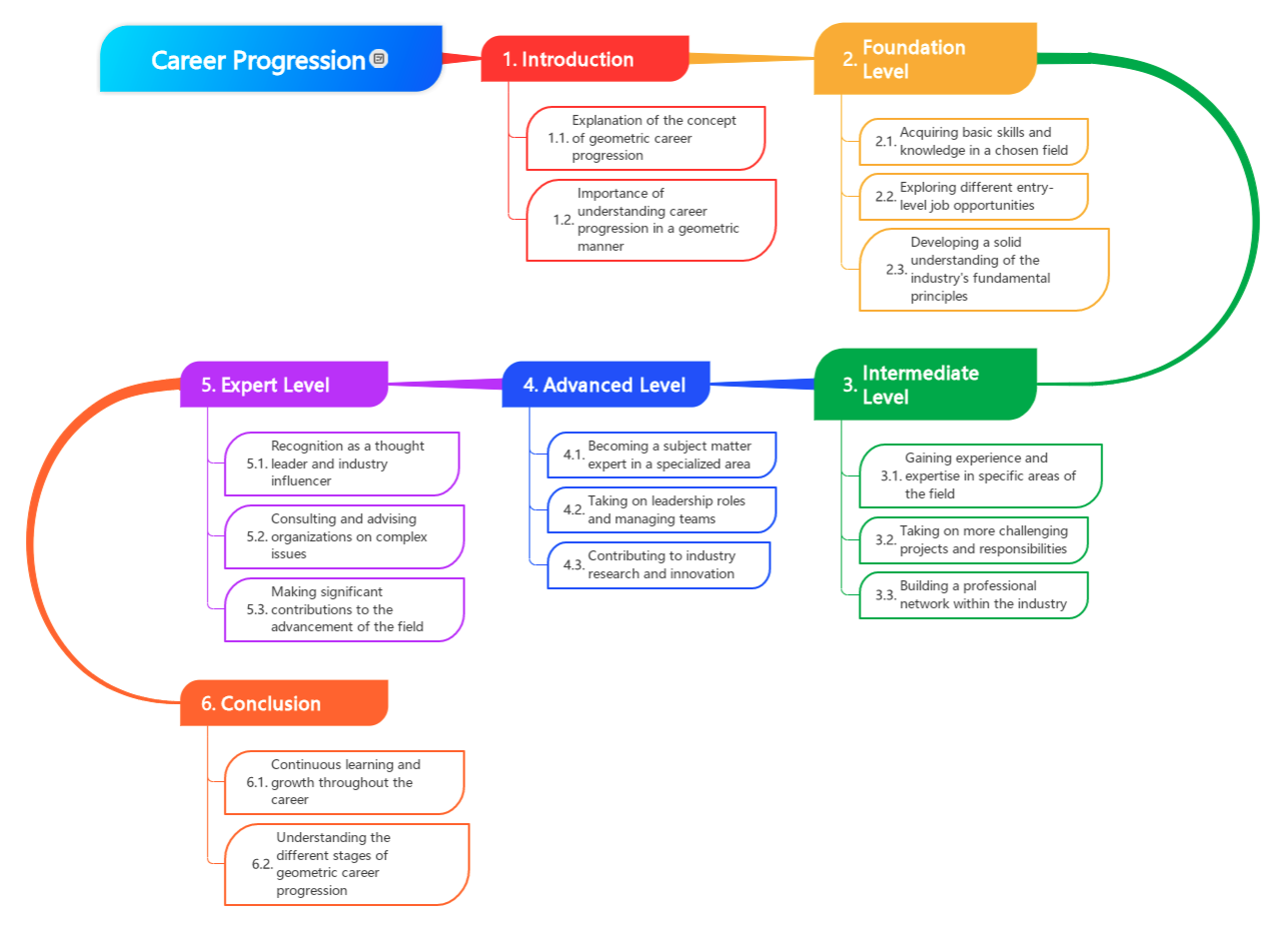
Summary : A career progression shows that the how professionals in different fields can grow their careers step-by-step, much like geometric patterns, where each step can significantly increase the scale, scope, or impact of their role and responsibilities.
This differs from linear career progression, which is gradual. Given the rapid pace of technological advancement and the need for continuous learning and adaptation, geometric career progression is relevant in software engineering and product management.
- Entry Level : (1) Acquiring basic skills and knowledge in a chosen field. (2) Exploring different entry-level job opportunities.(3)Developing a solid understanding of the industry’s fundamental principles.
- Intermediate Level: (1) Gaining experience and expertise in specific areas of the field.(2) Taking on more challenging projects and responsibilities.(3) Building a professional network within the industry.
- Advanced Level: (1) Becoming a subject matter expert in a specialized area. (2) Taking on leadership roles and managing teams. (3) Contributing to industry research and innovation.
- Expert Level: (2) Recognition as a thought leader and industry influencer. (2) Consulting and advising organizations on complex issues (3) Making significant contributions to the advancement of the field.
- Conclusion:(1) Continuous learning and growth throughout the career (2) Understanding the different stages of geometric career progression.
Software and Application Development Professionals Profiles:
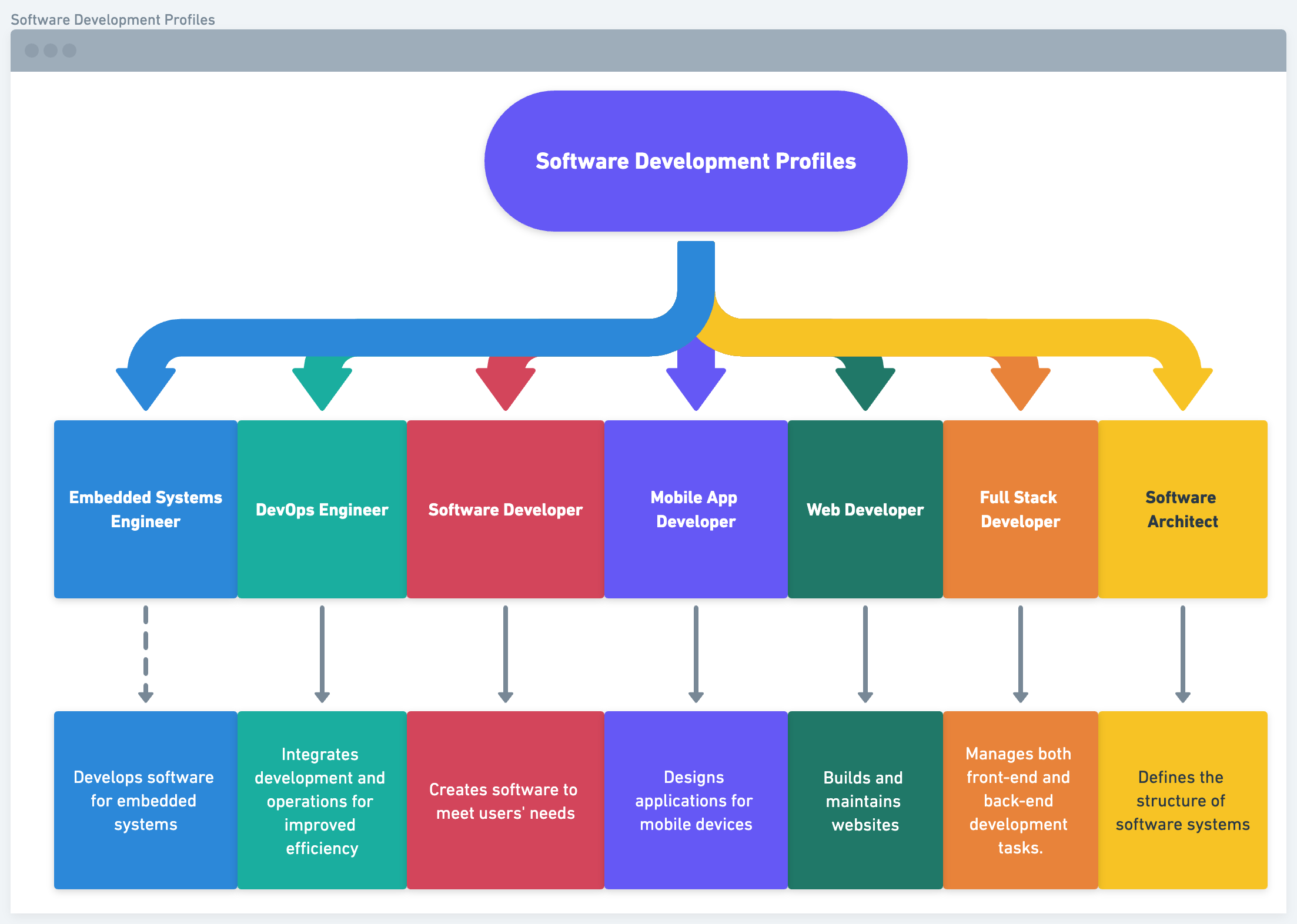
Software and Application Development is an important part of the IT world because it makes the digital products and tools that we use every day. It includes a lot of important job roles, like Software Developers who make custom software and Mobile App Developers who make apps for mobile devices. Web Developers build and maintain websites, and Full Stack Developers manages both front-end and back-end development tasks. DevOps Engineers speed up the process of making software, Software Architects plan how software systems are put together, and Embedded Systems Engineers work on connecting software to real-world devices. All together, these experts make digital innovations that are used in many parts of our lives. Here are top 7 job profiles for software and application development.
Please click the below list to get the specific details.
- Software Developer: Creates software to meet users’ needs.
- Mobile App Developer: Designs applications for mobile devices.
- Web Developer: Builds and maintains websites.
- Full Stack Developer: Manages both front-end and back-end development tasks.
- DevOps Engineer: Integrates development and operations for improved efficiency.
- Software Architect: Defines the structure of software systems.
- Embedded Systems Engineer: Develops software for embedded systems.
Data Science and Analytics Professionals Profiles :
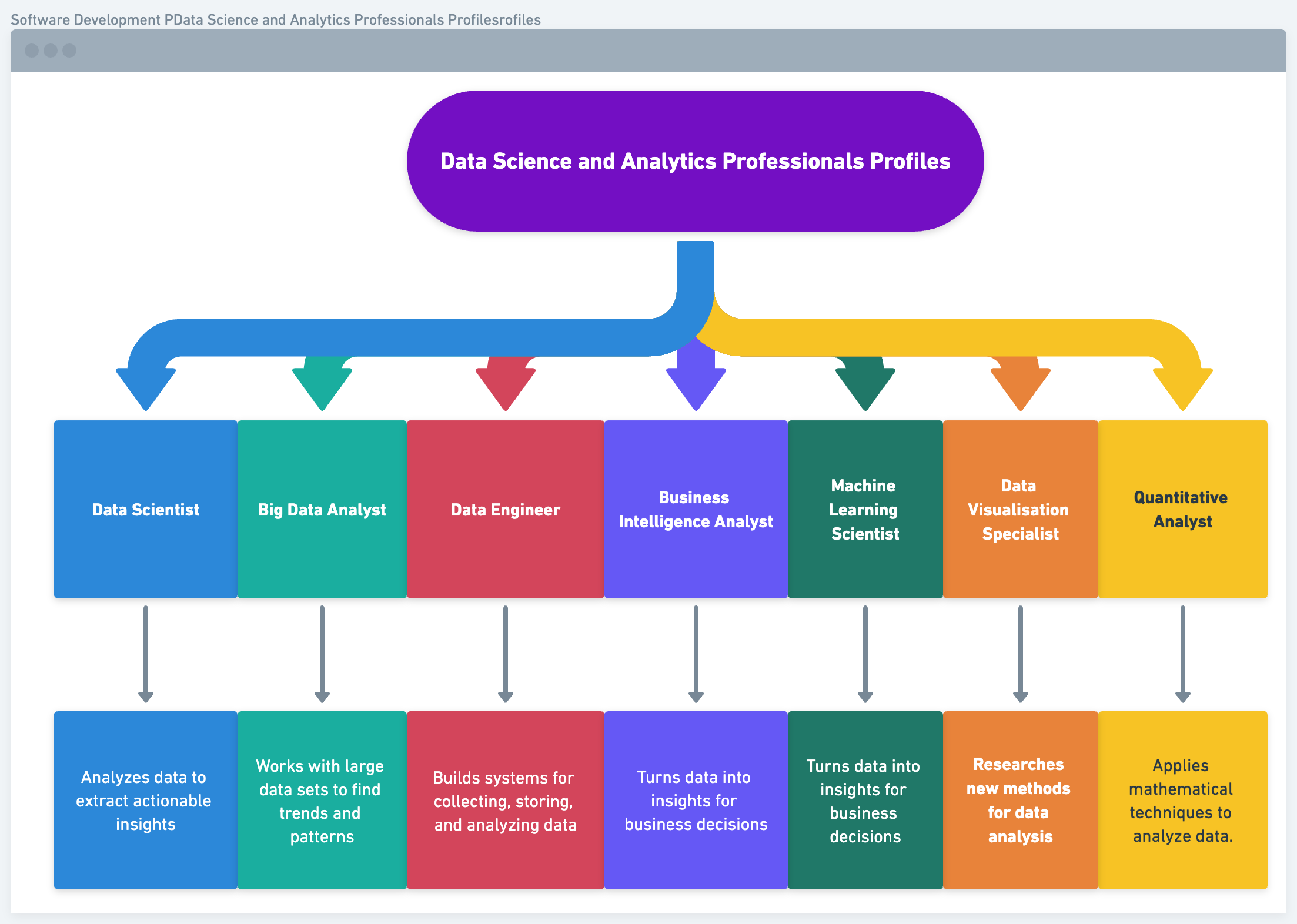
Here are the top 7 job profiles for professionals in data science and analytics.
- Data Scientist: Analyzes data to extract actionable insights.
- Big Data Analyst: Works with large data sets to find trends and patterns.
- Data Engineer: Builds systems for collecting, storing, and analyzing data.
- Business Intelligence Analyst: Turns data into insights for business decisions.
- Machine Learning Scientist: Researches new methods for data analysis.
- Data Visualization Specialist: Creates visual representations of data.
- Quantitative Analyst: Applies mathematical techniques to analyze data.
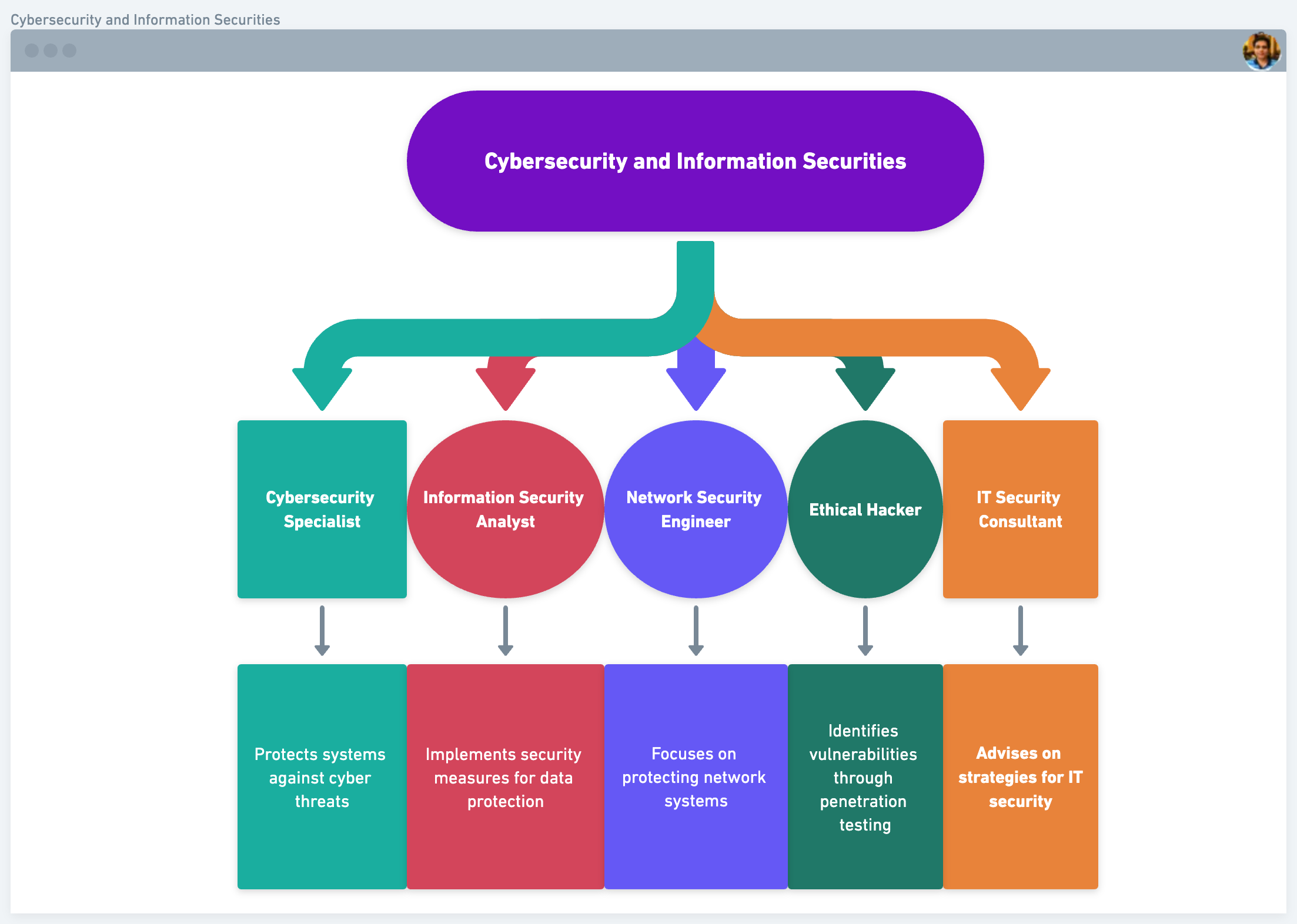
Cybersecurity and Information Securities:
- Cybersecurity Specialist: Protects systems against cyber threats.
- Information Security Analyst: Implements security measures for data protection.
- Network Security Engineer: Focuses on protecting network systems.
- Ethical Hacker: Identifies vulnerabilities through penetration testing.
- IT Security Consultant: Advises on strategies for IT security.
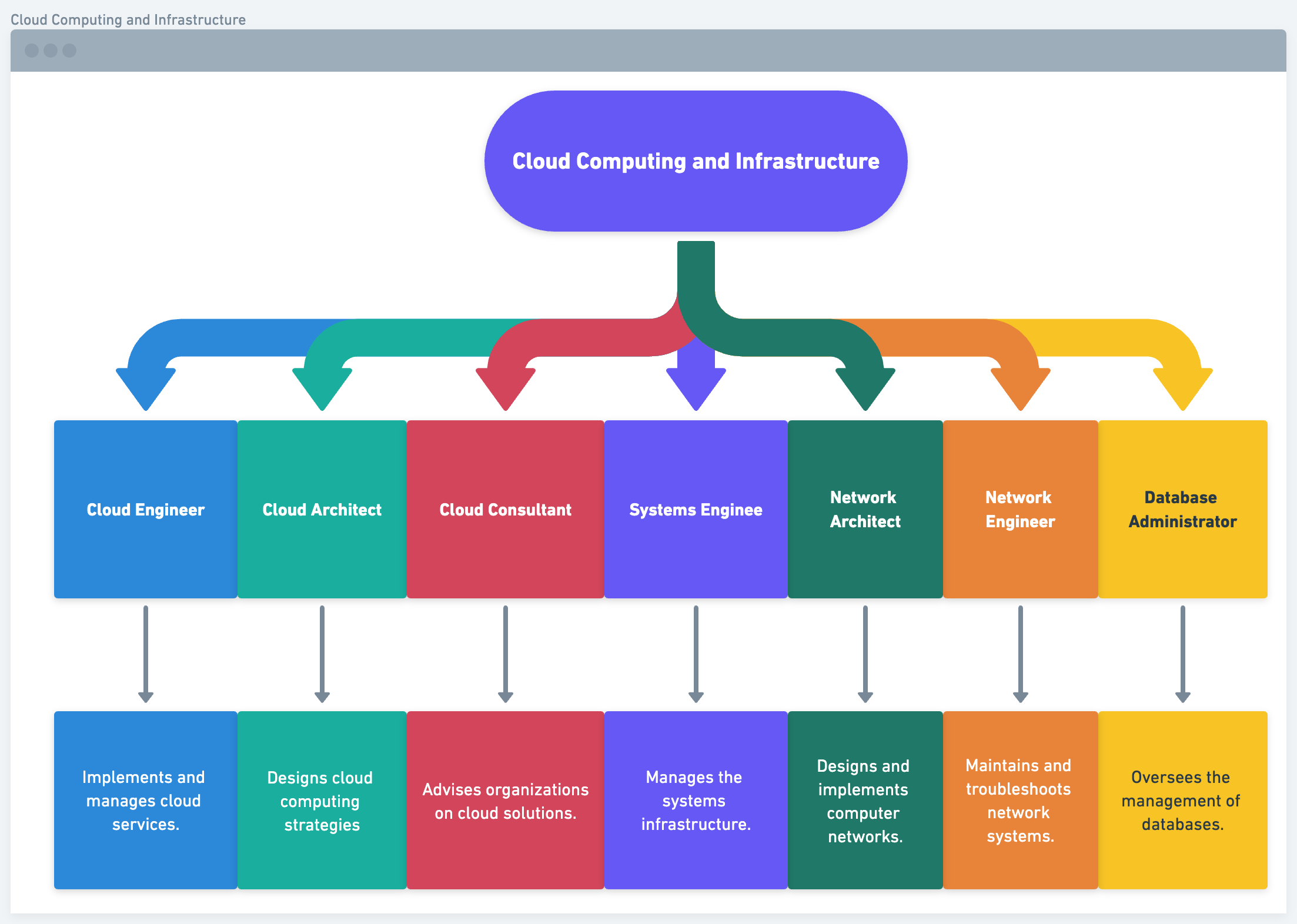
Cloud Computing and Infrastructure:
- Cloud Engineer: Implements and manages cloud services.
- Cloud Architect: Designs cloud computing strategies.
- Cloud Consultant: Advises organizations on cloud solutions.
- Systems Engineer: Manages the systems infrastructure.
- Network Architect: Designs and implements computer networks.
- Network Engineer: Maintains and troubleshoots network systems.
- Database Administrator: Oversees the management of databases.
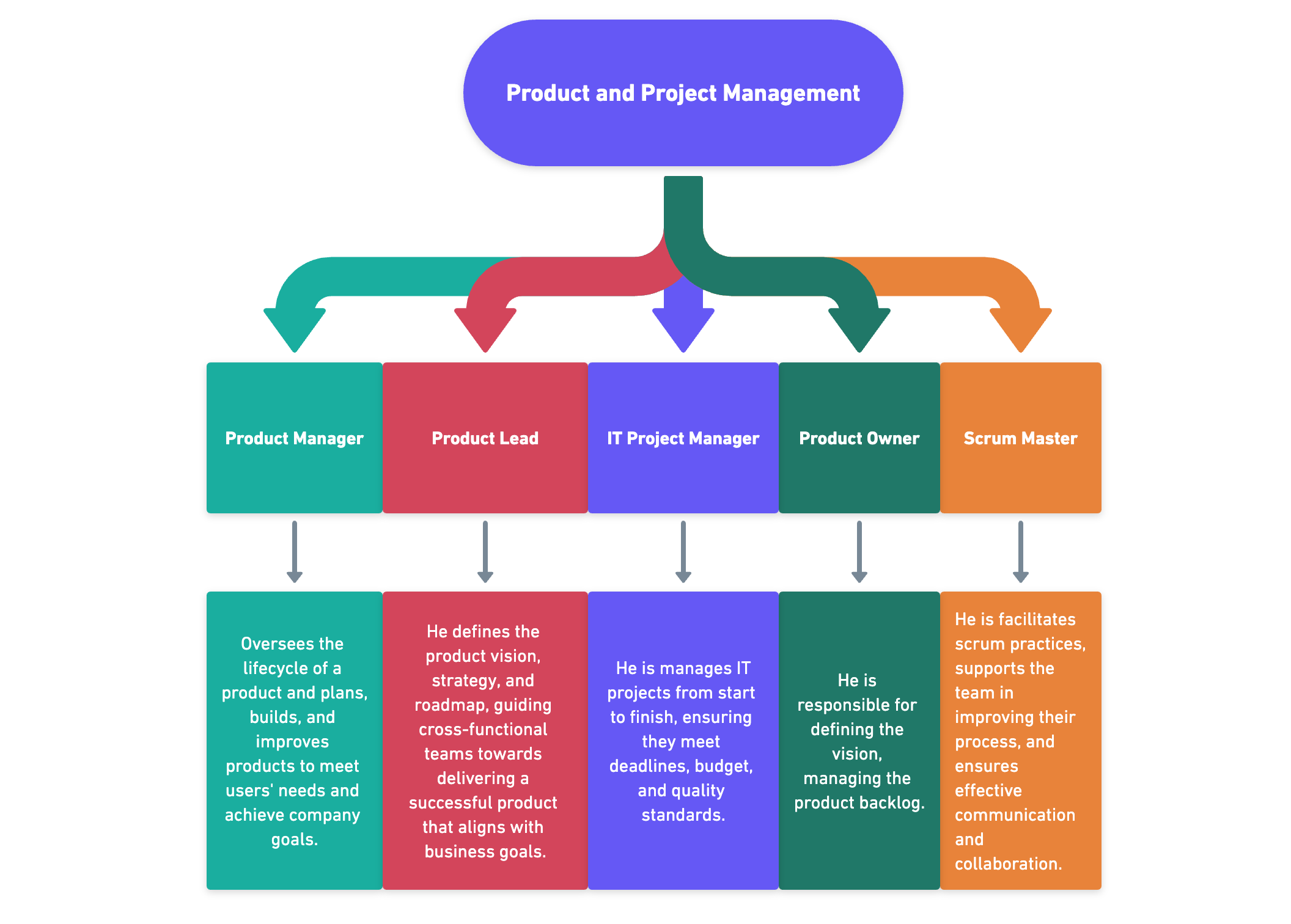
Product and Project Management:
- Product Manager: Oversees the lifecycle of a product and plans, builds, and improves products to meet users’ needs and achieve company goals.
- Product Lead:A product lead defines the product vision, strategy, and roadmap, guiding cross-functional teams towards delivering a successful product that aligns with business goals.
- IT Project Manager: Manages IT projects from conception to completion.
- Product Owner :He is responsible for defining the vision, managing the product backlog.
- Scrum Master: He is facilitates scrum practices, supports the team in improving their process, and ensures effective communication and collaboration.
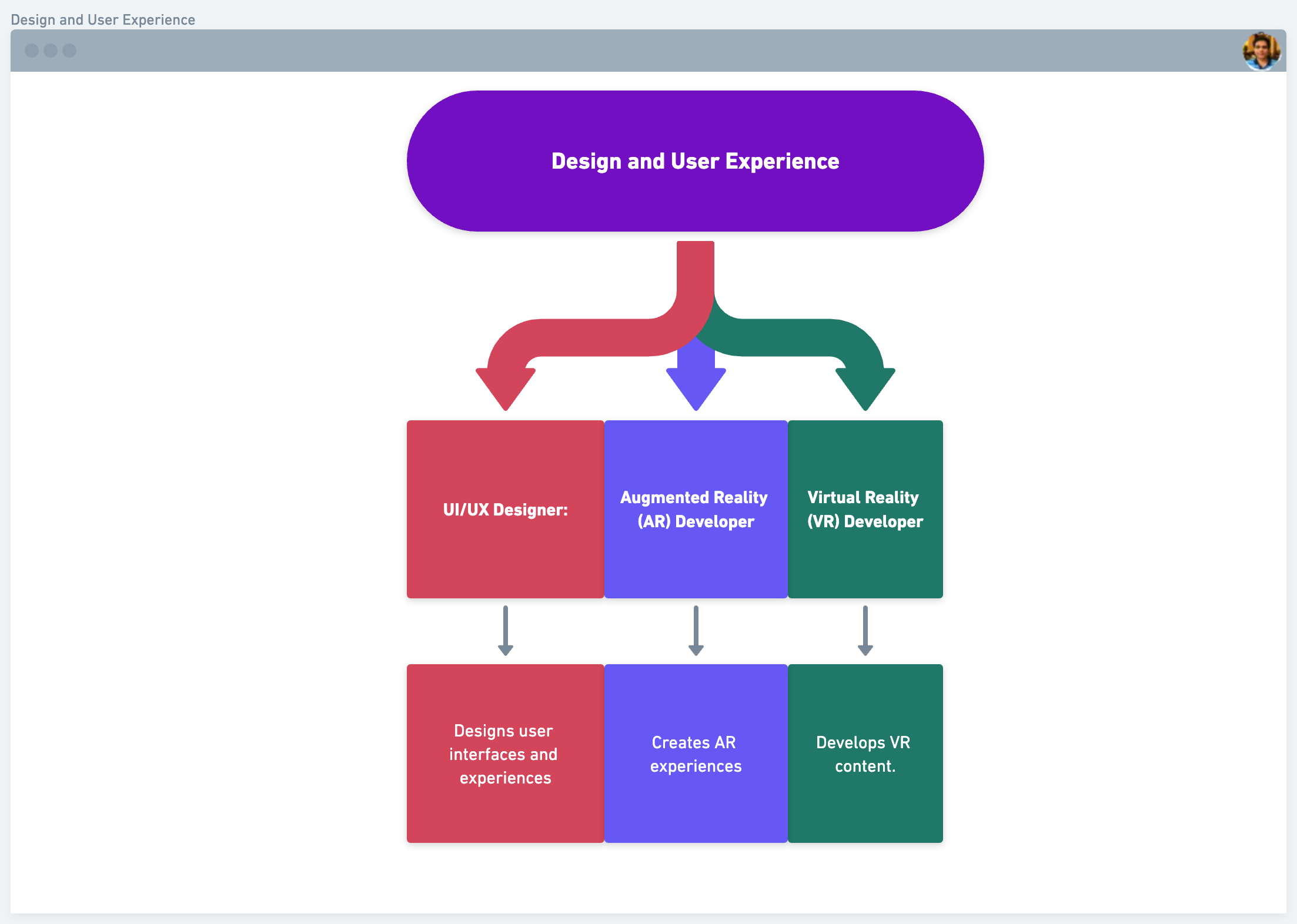
Design and User Experience:
- UI/UX Designer: Designs user interfaces and experiences.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Developer: Creates AR experiences.
- Virtual Reality (VR) Developer: Develops VR content.
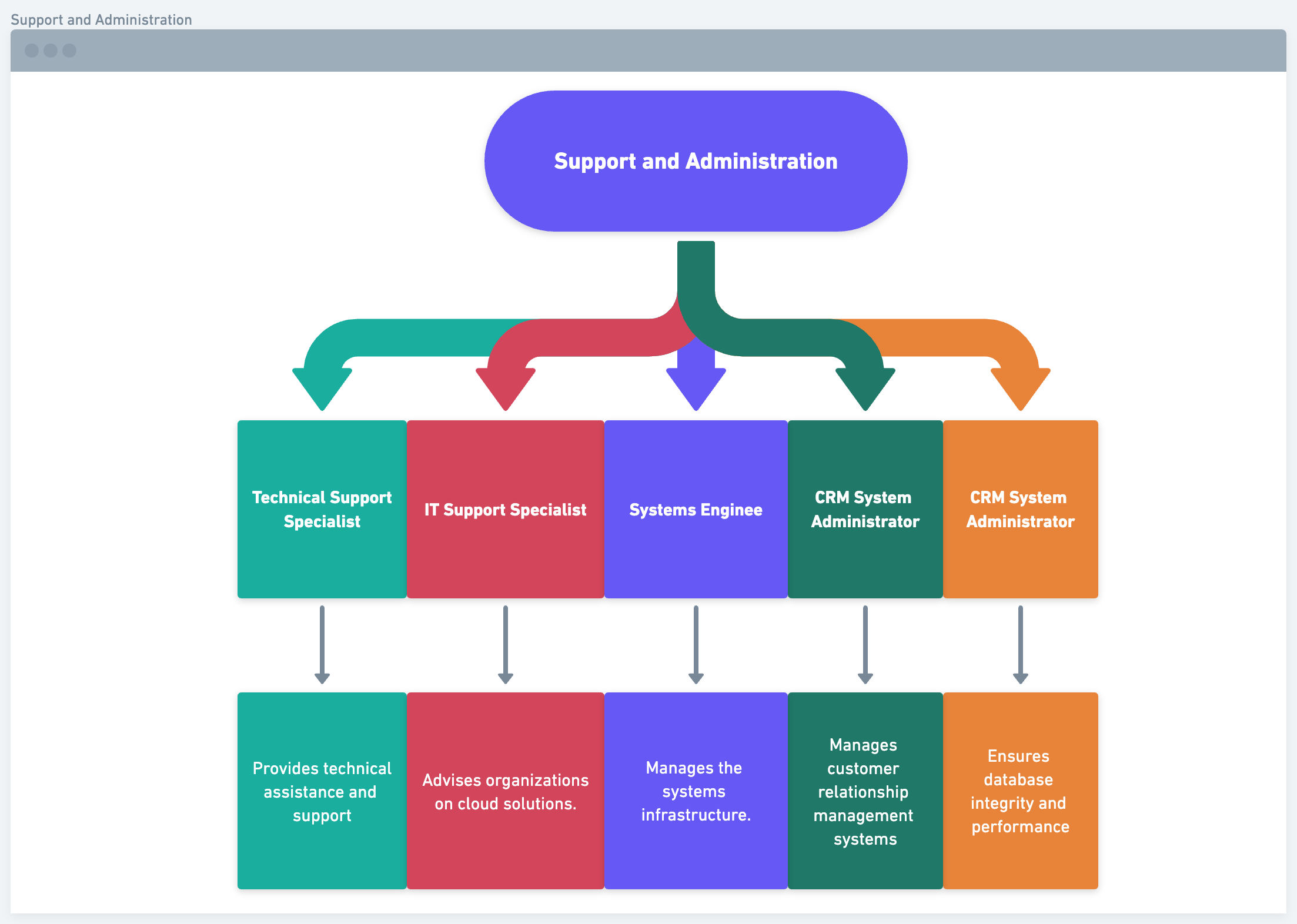
Support and Administration:
- Technical Support Specialist: Provides technical assistance and support.
- IT Support Specialist: Helps maintain IT systems’ functionality.
- Systems Analyst: Evaluates and improves IT systems.
- CRM System Administrator: Manages customer relationship management systems.
- Database Administrator: Ensures database integrity and performance.
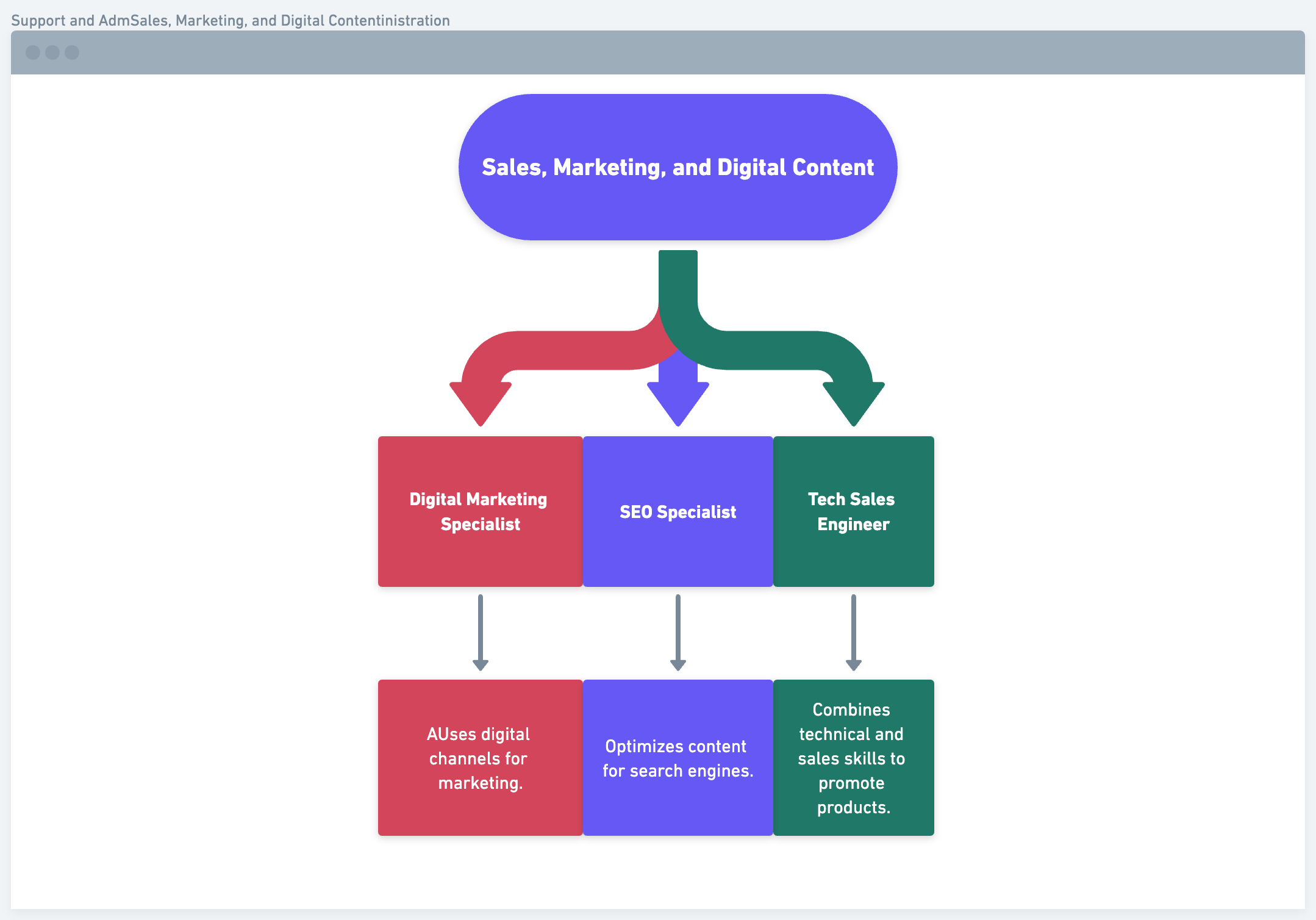
Sales, Marketing, and Digital Content:
- Digital Marketing Specialist: Uses digital channels for marketing.
- SEO Specialist: Optimizes content for search engines.
- Tech Sales Engineer: Combines technical and sales skills to promote products.
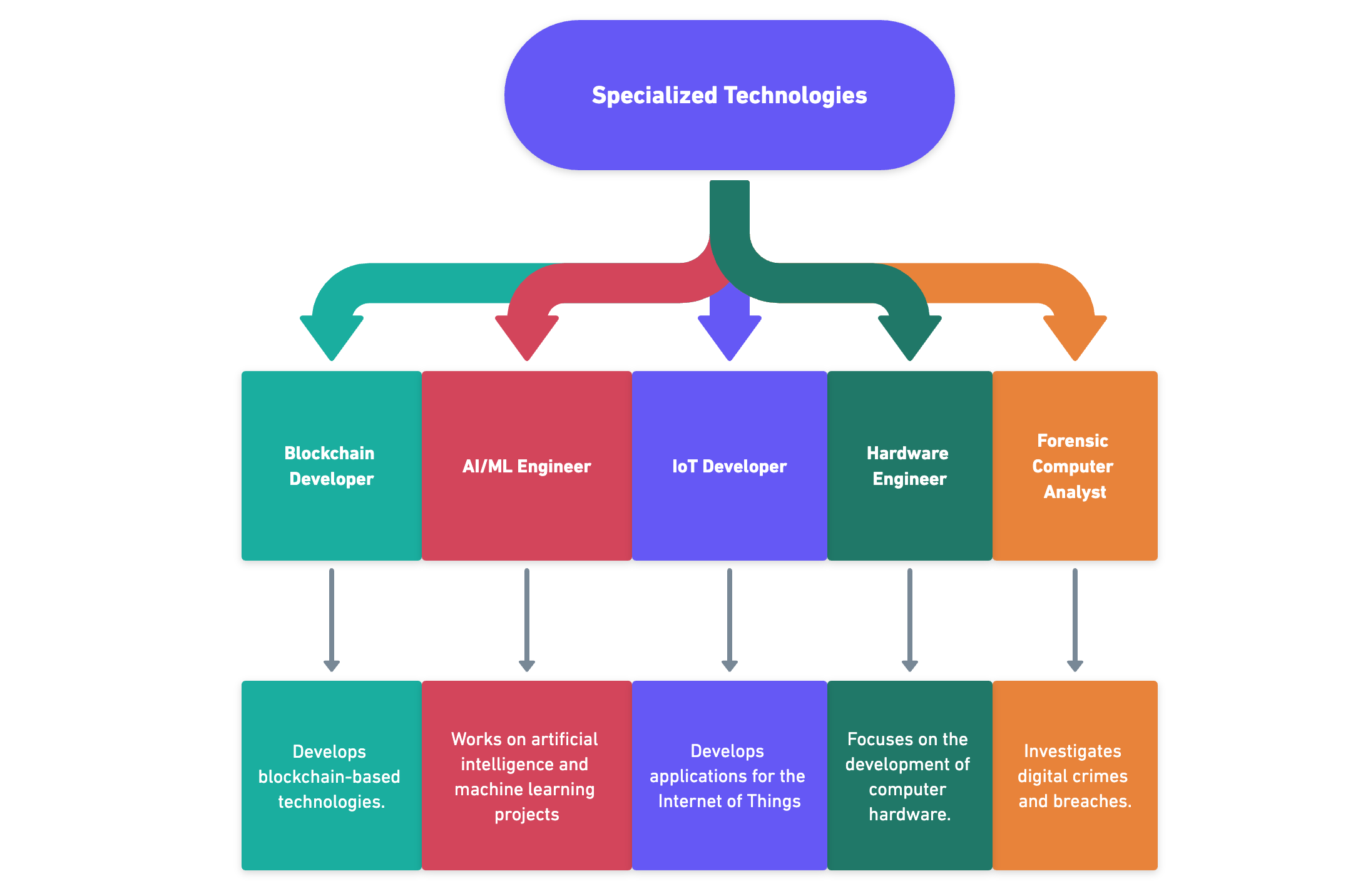
Specialized Technologies:
- Blockchain Developer: Develops blockchain-based technologies.
- AI/ML Engineer: Works on artificial intelligence and machine learning projects.
- IoT Developer: Develops applications for the Internet of Things.
- Hardware Engineer: Focuses on the development of computer hardware.
- Forensic Computer Analyst: Investigates digital crimes and breaches.
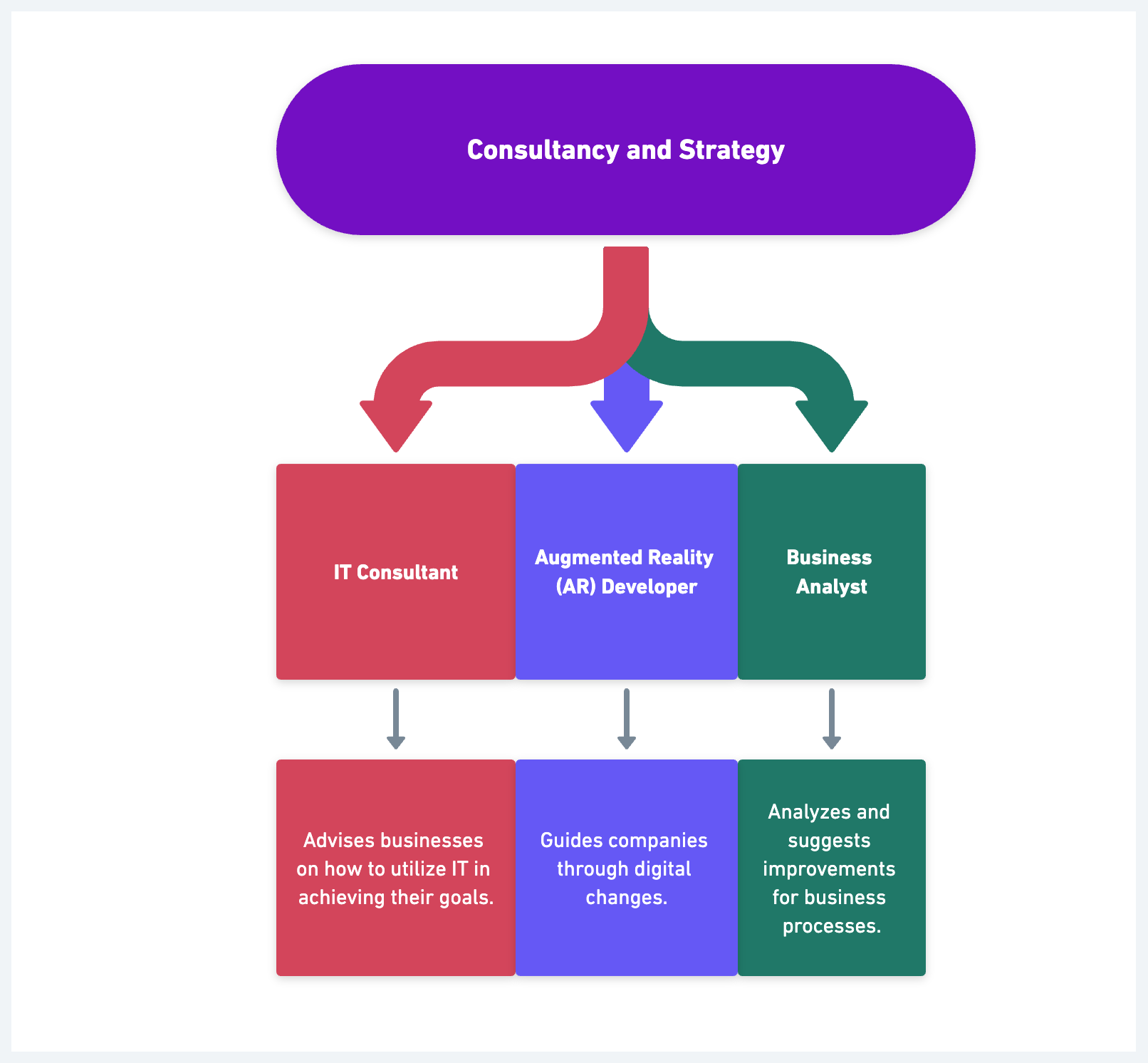
Consultancy and Strategy:
- IT Consultant: Advises businesses on how to utilize IT in achieving their goals.
- Digital Transformation Consultant: Guides companies through digital changes.
- Business Analyst: Analyzes and suggests improvements for business processes.
Emerging Technologies:
- Quantum Computing Researcher: (Added for completion) Investigates quantum computing technologies.