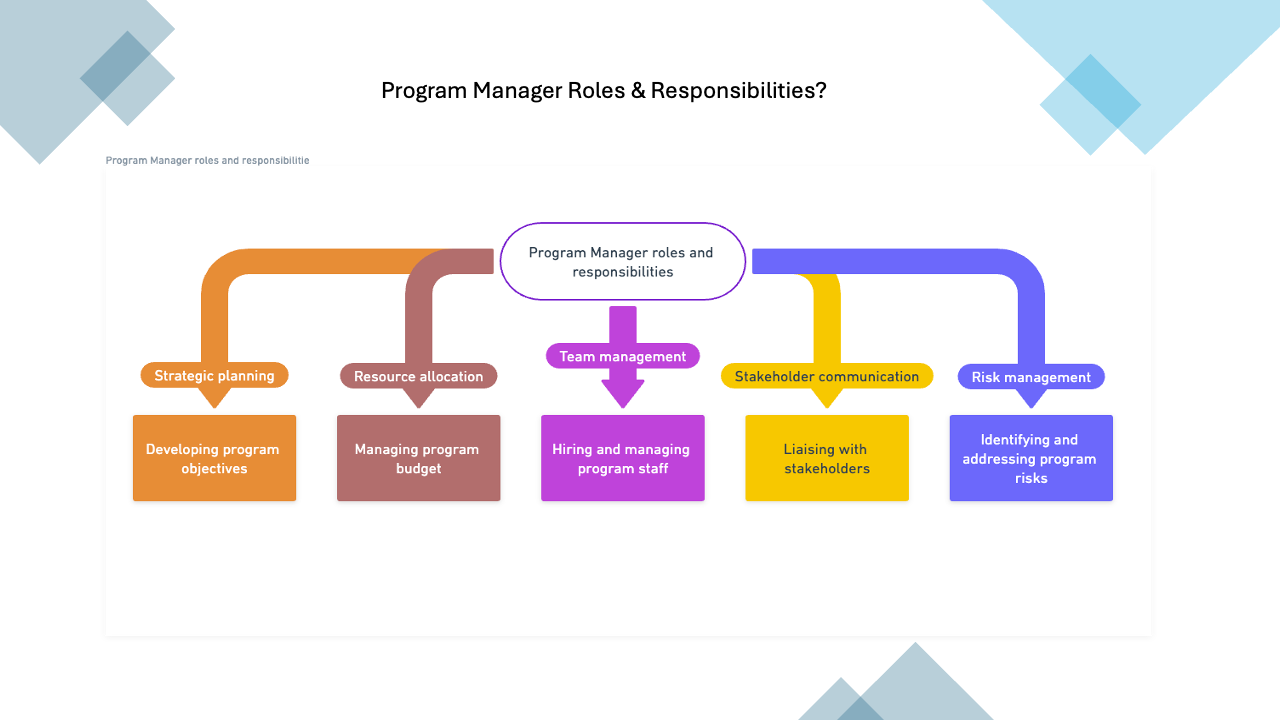
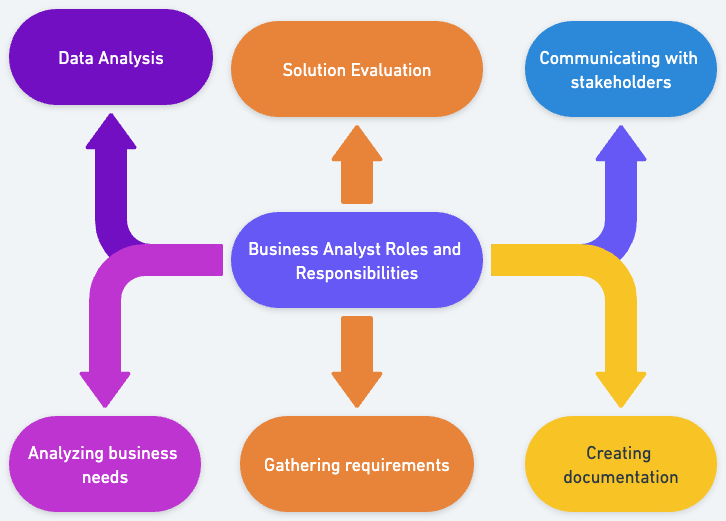
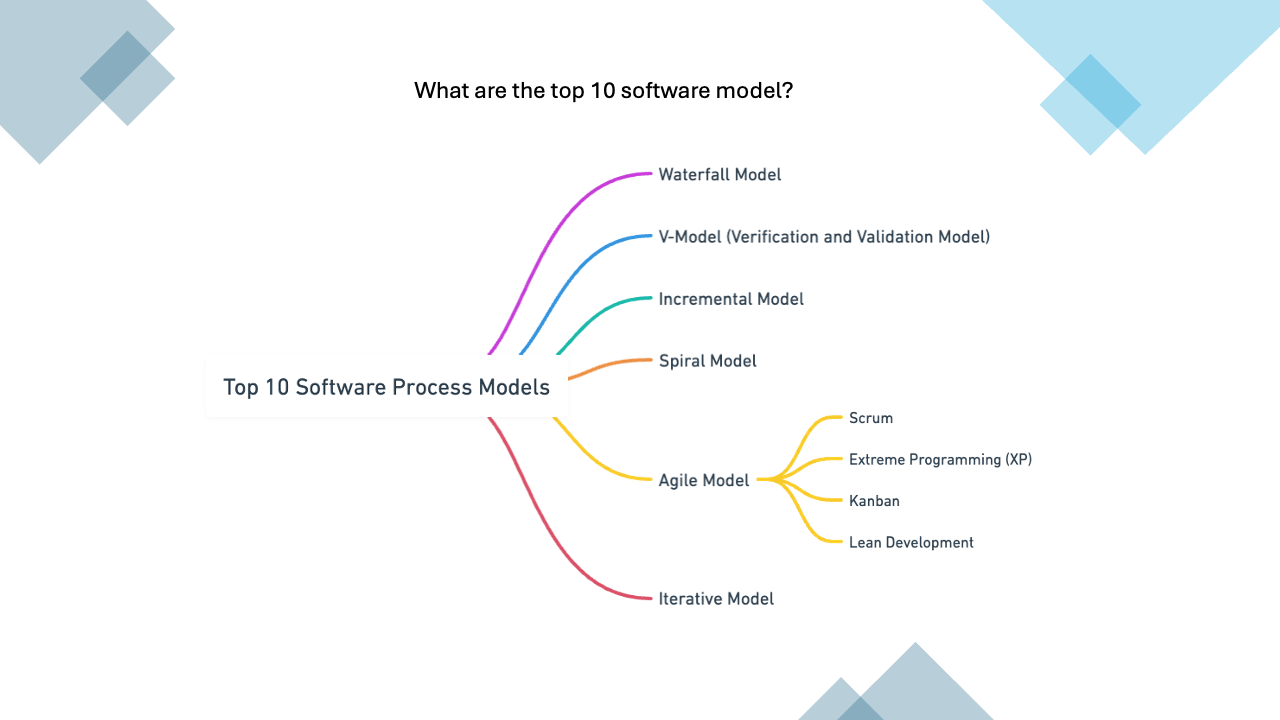
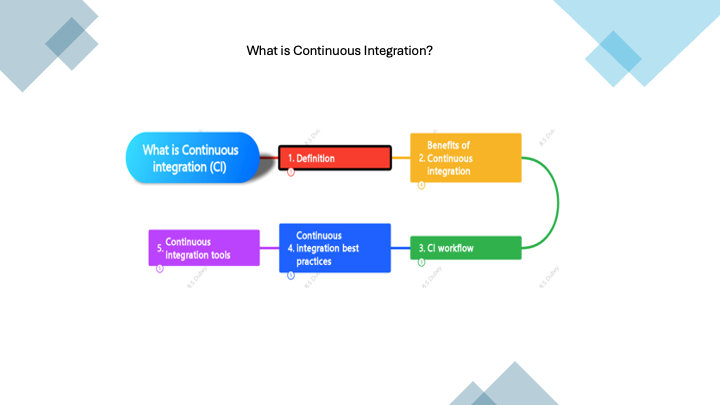
Business Analyst Roles & Responsibilities interview?
Business Analysts play a crucial role in bridging the gap between IT and the business, using data analytics to assess processes, determine requirements, and deliver data-driven recommendations and reports to executives and stakeholders.T
Turning numbers and data into actionable plans. Making sense of all that data and making smart moves to improve or speed things up. Share stories where you overcame obstacles, united everyone, and saw your ideas make a difference.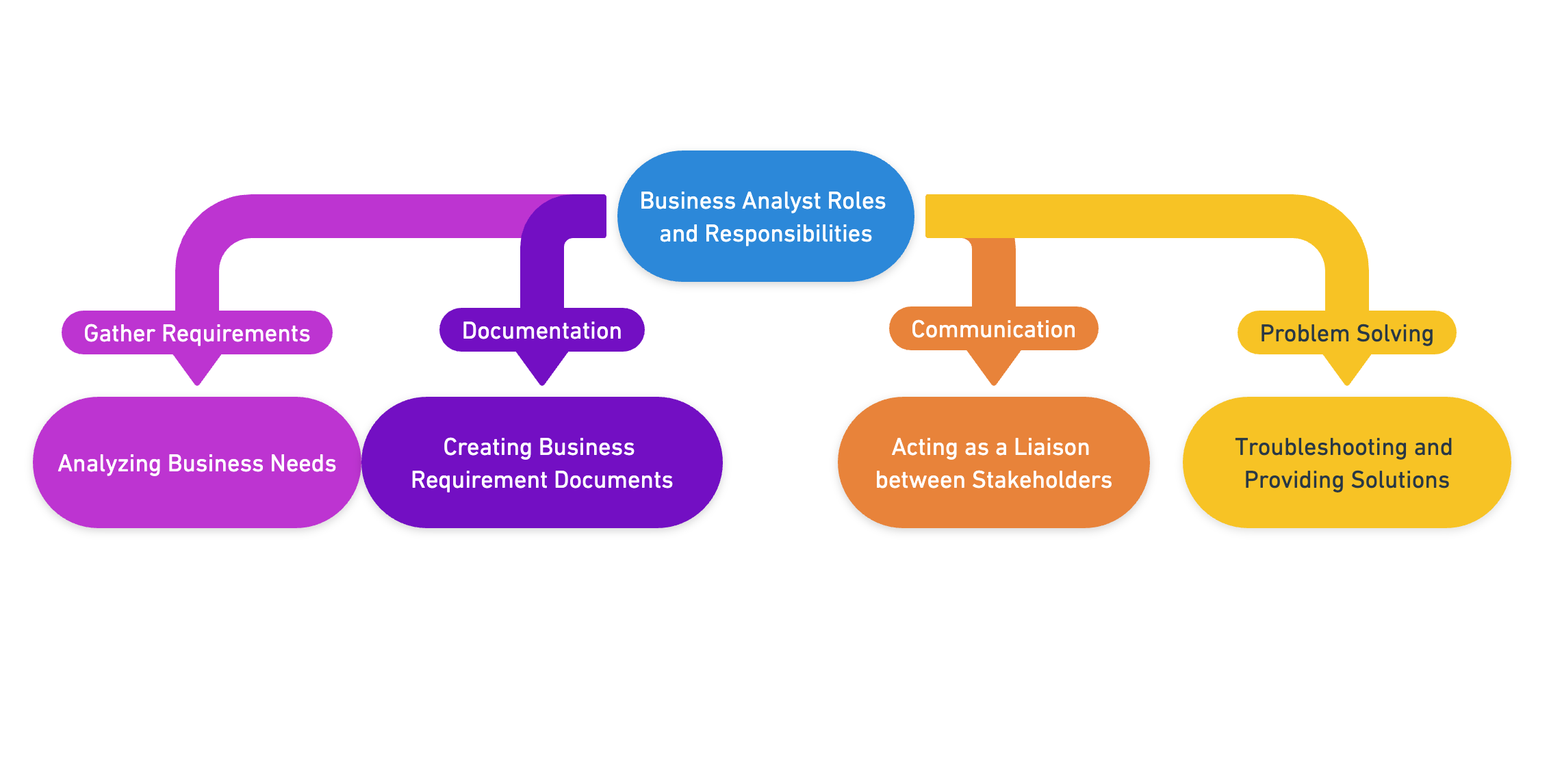
Ten(X) Factors: Catalysts for Business Analyst Career Growth