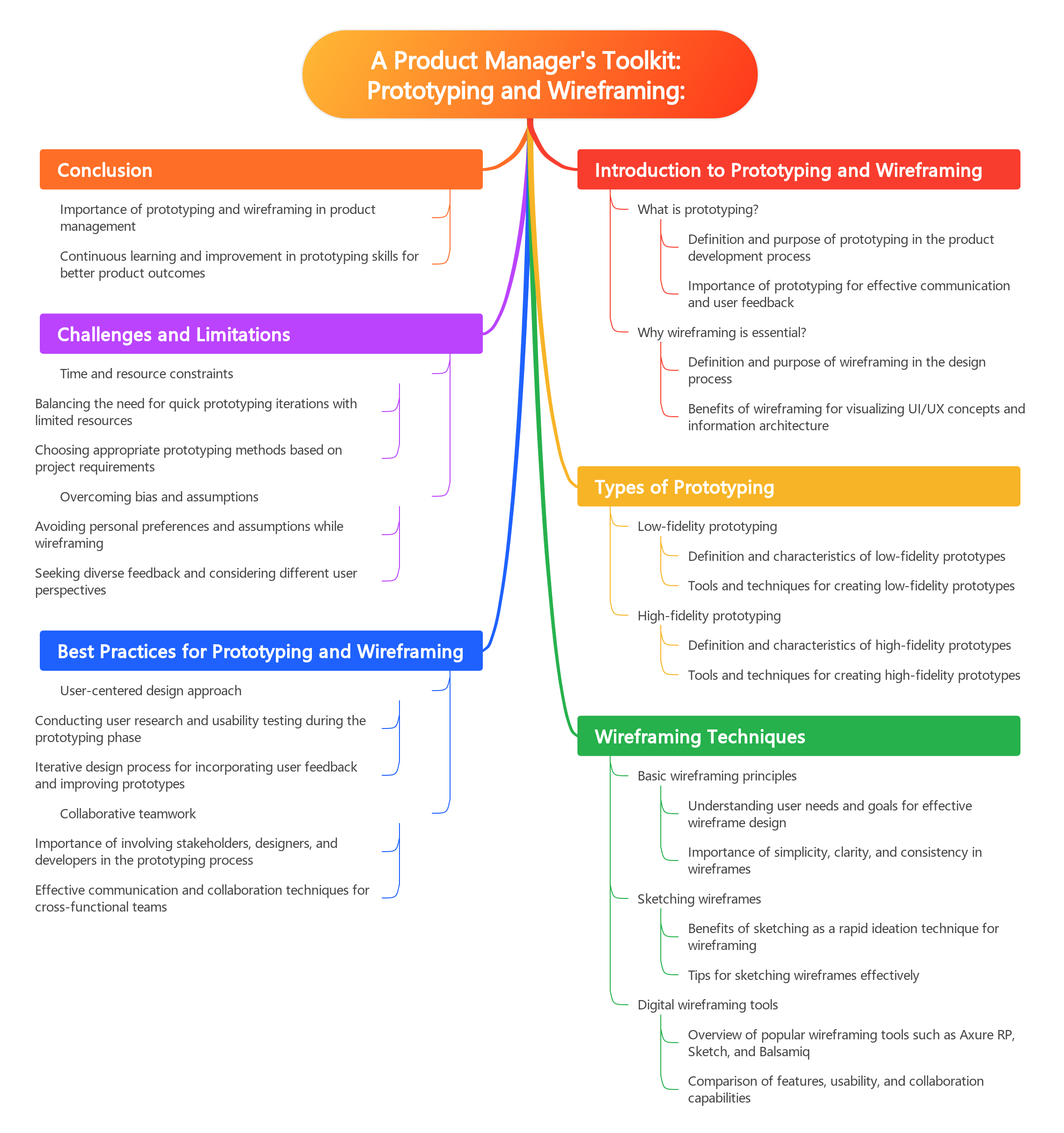
Prototyping and Wireframing: A Product Manager’s Toolkit
1: Introduction to Prototyping and Wireframing
The Importance of Prototyping in Product Development
As a Product Manager working in the niches of prototyping and wireframing, understanding the importance of prototyping in product development is crucial. Prototyping plays a key role in the product development process as it allows you to quickly visualize and test out ideas before investing significant time and resources into building a final product. In this subchapter, we will delve into the significance of prototyping and how it can benefit your product development efforts.
First and foremost, prototyping helps to mitigate risk in product development. By creating a prototype, you can identify potential issues and challenges early on in the process, allowing you to make necessary adjustments and improvements before moving forward. This can save you time and money in the long run by avoiding costly mistakes that may arise during the later stages of development.
Additionally, prototyping allows you to gather valuable feedback from stakeholders and users. By sharing your prototype with key stakeholders, such as team members, clients, and investors, you can solicit their input and insights to ensure that the final product meets their needs and expectations. User testing with prototypes can also provide valuable insights into how users interact with the product, allowing you to make informed decisions about its design and functionality.
Prototyping can also help to streamline the product development process by promoting collaboration and communication among team members. By creating a tangible representation of the product early on, team members can better understand the vision and goals of the project, leading to more efficient decision-making and problem-solving. Prototypes serve as a common reference point for discussions, helping to align team members on the project’s direction.
Furthermore, prototyping can help to spark creativity and innovation in product development. By experimenting with different ideas and concepts through prototyping, you can explore new possibilities and push the boundaries of what is possible. Prototyping allows you to iterate quickly and explore various design options, fostering a culture of innovation within your team.
In conclusion, the importance of prototyping in product development cannot be overstated. Prototyping helps to mitigate risk, gather feedback, streamline the development process, and spark creativity and innovation. By incorporating prototyping into your product development toolkit, you can accelerate the development process, improve the quality of the final product, and increase the chances of success in the marketplace. As a Product Manager working in the niches of prototyping and wireframing, embracing prototyping as a fundamental aspect of your workflow can lead to more successful and innovative products.
Understanding Wireframing in the Design Process
Understanding wireframing in the design process is crucial for product managers in the field of prototyping and wireframing. Wireframing is a key step in the product development process that allows designers and product managers to visually represent the layout and functionality of a digital product before any code is written. By creating wireframes, product managers can communicate their ideas more clearly to stakeholders, developers, and designers, ensuring that everyone is on the same page before moving forward with the project.
One of the main benefits of wireframing is that it allows product managers to quickly iterate on design ideas without investing a lot of time and resources. By creating low-fidelity wireframes, product managers can test different layouts, features, and user interactions to see what works best for the product. This rapid prototyping process helps identify potential issues early on in the design process, saving time and money in the long run.
Wireframing also helps product managers prioritize features and functionality by providing a visual representation of the product’s layout and flow. By creating wireframes, product managers can see how different elements of the product interact with each other and make informed decisions about what features are most important to include in the final product. This helps streamline the design process and ensures that the final product meets the needs of both the users and the business.
In addition to helping product managers communicate their ideas more effectively, wireframing also helps streamline the collaboration process between designers, developers, and other stakeholders. By creating wireframes, product managers can provide a visual reference for the entire team to work from, ensuring that everyone is aligned on the project’s goals and objectives. This collaborative approach helps reduce misunderstandings and conflicts between team members, leading to a more efficient and successful design process.
Overall, understanding wireframing in the design process is essential for product managers in the field of prototyping and wireframing. By creating wireframes, product managers can communicate their ideas more clearly, iterate on design ideas quickly, prioritize features and functionality, and streamline collaboration with designers, developers, and other stakeholders. By incorporating wireframing into their design process, product managers can create better products that meet the needs of both the users and the business.
2: Types of Prototyping Methods
Low-Fidelity Prototypes
In the world of product management, prototyping and wireframing are essential tools for bringing ideas to life and testing them with users. One type of prototype that is particularly useful in the early stages of product development is a low-fidelity prototype. Low-fidelity prototypes are quick and easy to create, allowing product managers to iterate on ideas rapidly without getting bogged down in details.
Low-fidelity prototypes are typically created using simple materials such as paper, sticky notes, or digital tools like wireframing software. These prototypes are intentionally rough and unfinished, focusing on the core functionality of a product rather than on design details. By keeping things simple, product managers can quickly test ideas with users and gather feedback to inform the next iteration of the prototype.
One of the key benefits of low-fidelity prototypes is that they can be created and tested quickly and cheaply. This allows product managers to experiment with different ideas and concepts without investing a lot of time or resources. By getting feedback early in the development process, product managers can identify potential issues and make necessary changes before moving on to more polished prototypes.
Another advantage of low-fidelity prototypes is that they encourage collaboration and communication within a team. Because these prototypes are easy to create and modify, team members can work together to explore different ideas and concepts. This collaborative approach can help to foster creativity and innovation, leading to better overall product outcomes.
In conclusion, low-fidelity prototypes are a valuable tool for product managers working in the fields of prototyping and wireframing. By creating quick and simple prototypes, product managers can test ideas with users, gather feedback, and iterate rapidly. This approach not only saves time and resources but also encourages collaboration and communication within a team. Ultimately, low-fidelity prototypes can help product managers to develop better products that meet the needs of their users.
High-Fidelity Prototypes
High-fidelity prototypes are an essential tool in the product manager’s toolkit when it comes to creating and testing new product concepts. These prototypes are highly detailed and closely resemble the final product in terms of functionality and design. They allow product managers to gather valuable feedback from stakeholders and users before moving forward with development.
One of the key benefits of high-fidelity prototypes is their ability to simulate the user experience with a high degree of accuracy. By incorporating realistic interactions and visual elements, product managers can get a better sense of how users will interact with the final product. This level of detail also helps to uncover any potential usability issues early on in the design process, saving time and resources in the long run.
In addition to gathering feedback from stakeholders and users, high-fidelity prototypes can also be used to conduct usability testing. By observing how users interact with the prototype, product managers can identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions about the final product design. This iterative approach to prototyping ensures that the final product meets user needs and expectations.
Creating high-fidelity prototypes requires a combination of design skills and technical knowledge. Product managers must work closely with designers and developers to bring their vision to life in a way that accurately represents the final product. This collaboration is essential for ensuring that the prototype is both functional and visually appealing, while also aligning with the overall product strategy.
In conclusion, high-fidelity prototypes play a crucial role in the prototyping and wireframing process for product managers. By creating detailed representations of the final product, product managers can gather valuable feedback, conduct usability testing, and make informed design decisions. This hands-on approach to prototyping helps to ensure that the final product meets user needs and expectations, ultimately leading to a more successful product launch.
Interactive Prototypes
Interactive prototypes are a crucial tool in the arsenal of any product manager when it comes to effectively communicating ideas and designs to stakeholders. By creating interactive prototypes, product managers can provide a tangible representation of how a product will look and function, allowing for clearer feedback and faster decision-making processes.
One of the key benefits of interactive prototypes is their ability to simulate the user experience of a final product. By incorporating interactive elements such as clickable buttons, dropdown menus, and input fields, product managers can create a more immersive experience for stakeholders to interact with. This can help stakeholders better understand the flow of the product and identify any potential pain points or areas for improvement.
Interactive prototypes also allow for rapid iteration and testing of design ideas. By creating multiple versions of a prototype and gathering feedback from stakeholders, product managers can quickly refine and improve the design before moving on to the development phase. This iterative process can help save time and resources in the long run by catching potential issues early on in the design process.
Furthermore, interactive prototypes can be used to conduct usability testing with real users. By observing how users interact with the prototype and gathering feedback on their experience, product managers can gain valuable insights into how the product can be improved to better meet the needs of its target audience. This user-centered approach can lead to a more successful product launch and higher user satisfaction.
In conclusion, interactive prototypes are an essential tool for product managers in the prototyping and wireframing process. By creating interactive representations of their designs, product managers can effectively communicate ideas, gather feedback, iterate quickly, and conduct usability testing. Ultimately, interactive prototypes can help product managers create better products that meet the needs of their target audience.
3: Tools for Prototyping and Wireframing
Sketch
In the world of prototyping and wireframing, sketching is an essential tool for product managers. Sketching allows product managers to quickly and easily visualize ideas and concepts before diving into more detailed prototyping. Sketching can be done on paper or digitally, depending on personal preference and resources available. Regardless of the method used, sketching is a valuable skill that every product manager should master.
Sketching is a great way to brainstorm and generate new ideas for products or features. By quickly sketching out different concepts, product managers can explore various possibilities and iterate on designs before committing to a final prototype. Sketching also helps product managers communicate their ideas more effectively to stakeholders and team members, as sketches can often convey complex concepts more clearly than words alone.
One of the key benefits of sketching is its speed and flexibility. Unlike more detailed prototyping tools, sketching allows product managers to quickly jot down ideas and make changes on the fly. This agility is especially useful in the early stages of product development when ideas are still being fleshed out and refined. By sketching out multiple concepts, product managers can compare and contrast different ideas to determine the best direction for their product.
Sketching is also a valuable tool for validating ideas with users. By creating rough sketches of potential designs or features, product managers can gather feedback from users early in the development process. This feedback can then be used to refine and improve the final product, ultimately leading to a better user experience. In this way, sketching serves as a bridge between ideation and implementation, helping product managers to create products that truly meet the needs of their users.
In conclusion, sketching is a powerful tool for product managers working in the realms of prototyping and wireframing. By mastering the art of sketching, product managers can quickly generate new ideas, communicate concepts effectively, and validate designs with users. Whether done on paper or digitally, sketching is a versatile and indispensable skill that every product manager should have in their toolkit.
Adobe XD
Adobe XD is a powerful tool that every product manager should have in their toolkit when it comes to prototyping and wireframing. This software allows you to create interactive prototypes that closely resemble the final product, making it easier to visualize and communicate your ideas to stakeholders and developers. With Adobe XD, you can quickly design and iterate on your product concepts, helping you to streamline the product development process.
One of the key features of Adobe XD is its ease of use. The intuitive interface allows even those with limited design experience to create professional-looking prototypes. The drag-and-drop functionality makes it simple to add elements such as buttons, images, and text to your designs. Additionally, Adobe XD offers a variety of pre-built UI kits and templates to help you get started quickly, saving you time and effort in the prototyping process.
Another benefit of using Adobe XD is its collaboration capabilities. Product managers can easily share their prototypes with team members and stakeholders, allowing for real-time feedback and comments. This collaborative approach helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that any necessary changes can be implemented quickly. Additionally, Adobe XD integrates seamlessly with other Adobe Creative Cloud products, making it easy to share assets and design files across different applications.
Adobe XD also offers a range of interactive features that enhance the prototyping experience. You can create interactive animations, transitions, and gestures to bring your designs to life. This allows you to test the usability of your product and gather valuable feedback from users before finalizing the design. By simulating the user experience, you can identify any potential issues or improvements early on in the development process, ultimately saving time and resources down the line.
In conclusion, Adobe XD is a valuable tool for product managers working in the prototyping and wireframing space. Its user-friendly interface, collaboration capabilities, and interactive features make it an essential asset for creating high-quality prototypes that accurately represent your product vision. By incorporating Adobe XD into your workflow, you can streamline the design process, improve communication with stakeholders, and ultimately deliver a more polished and user-friendly product.
InVision
InVision is a powerful prototyping tool that allows product managers to create interactive and realistic prototypes of their designs. This tool is essential for product managers in the prototyping and wireframing niche as it enables them to quickly and easily test out different design ideas and gather feedback from stakeholders. InVision provides a user-friendly interface that makes it easy to create and share prototypes with team members and clients.
One of the key features of InVision is the ability to create clickable prototypes that mimic the functionality of a real product. Product managers can easily add interactive elements such as buttons, links, and animations to their designs, allowing stakeholders to experience the product in a more realistic way. This is especially useful for testing out different user flows and interactions before committing to a final design.
In addition to creating interactive prototypes, InVision also offers collaboration tools that allow product managers to gather feedback from team members and clients. With InVision, product managers can easily share their prototypes with stakeholders and collect comments and suggestions directly within the platform. This streamlines the feedback process and ensures that everyone is on the same page when it comes to the design of the product.
Another benefit of using InVision is its integration with other design tools such as Sketch and Adobe XD. Product managers can easily import their designs from these tools into InVision and turn them into interactive prototypes with just a few clicks. This seamless integration makes it easy for product managers to incorporate InVision into their existing design workflows and streamline the prototyping process.
Overall, InVision is a valuable tool for product managers working in the prototyping and wireframing niche. Its intuitive interface, interactive features, and collaboration tools make it easy to create realistic prototypes and gather feedback from stakeholders. By incorporating InVision into their design workflows, product managers can streamline the prototyping process and ensure that their designs are user-friendly and effective.
4: Best Practices for Prototyping and Wireframing
Setting Clear Objectives
Setting clear objectives is crucial in the prototyping and wireframing process for product managers. Without a clear understanding of what the end goal is, it can be easy to get lost in the details and lose sight of the overall purpose of the project. By clearly defining objectives at the beginning of the process, product managers can ensure that everyone on the team is working towards the same goal and that the final product meets the needs of both the users and the business.
One of the first steps in setting clear objectives is to define the problem that the prototype or wireframe is trying to solve. This could be anything from improving the user experience of a website to streamlining a complex business process. By clearly articulating the problem, product managers can ensure that the team is focused on finding a solution that addresses the root cause of the issue, rather than just treating the symptoms.
Once the problem has been defined, product managers should work with their team to establish specific, measurable objectives for the project. These objectives should be achievable within a set timeframe and should align with the overall goals of the organization. By setting clear objectives, product managers can track progress throughout the prototyping and wireframing process and make adjustments as needed to ensure that the project stays on track.
In addition to setting objectives for the project as a whole, product managers should also establish goals for each individual prototype or wireframe. These goals should be tied back to the overall objectives of the project and should outline what the team hopes to achieve with each iteration. By setting clear goals for each prototype, product managers can ensure that the team is focused on making incremental progress towards the final product.
Finally, product managers should regularly review and update the objectives for the project as needed. As the prototyping and wireframing process progresses, new information may come to light that necessitates a change in direction or priorities. By regularly revisiting and updating the objectives for the project, product managers can ensure that the team remains focused on the most important tasks and that the final product meets the needs of both the users and the business.
Involving Stakeholders in the Process
As a Product Manager, involving stakeholders in the prototyping and wireframing process is crucial for the success of a project. Stakeholders are individuals or groups who have a vested interest in the product and can provide valuable insights and feedback throughout the development process. By including stakeholders early on in the process, you can ensure that their needs and requirements are taken into account, resulting in a more user-centric and successful product.
One way to involve stakeholders in the process is to hold regular meetings or workshops where they can provide feedback on the prototypes and wireframes. This can help ensure that the product meets their expectations and addresses any concerns or issues they may have. By actively involving stakeholders in the decision-making process, you can also build trust and buy-in for the final product, increasing the likelihood of its success.
Another way to involve stakeholders in the process is to gather feedback through surveys or interviews. This can help you understand their needs and preferences more deeply, allowing you to make informed decisions about the design and functionality of the product. By actively seeking out and incorporating stakeholder feedback, you can ensure that the final product meets their expectations and delivers value to the end user.
Involving stakeholders in the prototyping and wireframing process can also help to identify potential risks or challenges early on. By soliciting feedback from stakeholders, you can uncover any issues or concerns that may arise during development and address them before they become major roadblocks. This proactive approach can save time and resources in the long run, as it allows you to make necessary adjustments before moving forward with the project.
Overall, involving stakeholders in the prototyping and wireframing process is essential for product managers in the niches of prototyping and wireframing. By actively seeking out and incorporating stakeholder feedback, you can ensure that the final product meets their needs and expectations, builds trust and buy-in for the project, and identifies potential risks or challenges early on. By making stakeholders an integral part of the development process, you can increase the likelihood of creating a successful and user-centric product.
Iterating and Testing Designs
In the world of product management, iterating and testing designs is a crucial step in the development process. Prototyping and wireframing are essential tools that can help product managers refine their designs and gather valuable feedback from stakeholders and end-users. In this subchapter, we will explore the importance of iterating and testing designs, as well as best practices for using prototyping and wireframing to streamline this process.
Iterating on designs involves making incremental changes to a design based on feedback and testing results. By continuously refining and improving a design, product managers can ensure that the final product meets the needs and expectations of their target audience. Prototyping and wireframing allow product managers to quickly create and test multiple design iterations, enabling them to gather valuable insights and make informed decisions about the direction of the product.
Testing designs is an essential part of the iteration process, as it allows product managers to validate their assumptions and make data-driven decisions. By testing prototypes with real users, product managers can identify usability issues, gather feedback on features, and make informed design decisions. This feedback loop is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets the needs and expectations of users, ultimately leading to a more successful product launch.
When using prototyping and wireframing tools to iterate and test designs, product managers should focus on creating high-fidelity prototypes that accurately represent the final product. By incorporating interactive elements, animations, and realistic content, product managers can create prototypes that closely resemble the final product, allowing them to gather more accurate feedback from users. Additionally, product managers should involve stakeholders and end-users in the testing process to ensure that their feedback is incorporated into the design.
In conclusion, iterating and testing designs is a critical step in the product development process, and prototyping and wireframing are essential tools for streamlining this process. By continuously refining and testing design iterations, product managers can ensure that their final product meets the needs and expectations of their target audience. By incorporating feedback from stakeholders and end-users, product managers can make informed decisions about the design direction, ultimately leading to a more successful product launch.
5: Incorporating Prototyping into Product Management
Using Prototypes to Communicate Ideas
In the world of product management, communication is key. One of the most effective ways to communicate ideas and concepts to stakeholders is through the use of prototypes. Prototypes are tangible representations of a product or feature that allow stakeholders to see and interact with the design before it is fully developed. By using prototypes, product managers can gather feedback, validate ideas, and make informed decisions about the direction of a project.
Prototypes come in many forms, from simple sketches on paper to interactive digital mockups. Each type of prototype has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice will depend on the specific needs of the project. For example, low-fidelity prototypes, such as paper sketches or wireframes, are quick and easy to create and are great for exploring different design ideas. On the other hand, high-fidelity prototypes, such as interactive digital prototypes, provide a more realistic representation of the final product and are useful for testing user interactions and functionality.
When using prototypes to communicate ideas, it is important to involve stakeholders early and often in the process. By sharing prototypes with stakeholders early on, product managers can gather valuable feedback and ensure that everyone is aligned on the vision for the product. This early involvement can help to prevent misunderstandings and miscommunications later on in the project, saving time and resources in the long run.
In addition to gathering feedback, prototypes can also be used to validate ideas and test assumptions. By creating prototypes and testing them with users, product managers can quickly identify any usability issues or design flaws and make necessary adjustments before investing time and resources into development. This iterative approach can help to ensure that the final product meets the needs and expectations of users and stakeholders.
Overall, prototypes are powerful tools for product managers to communicate ideas, gather feedback, validate assumptions, and make informed decisions. By incorporating prototypes into their workflow, product managers can increase the likelihood of success for their projects and create products that delight users and stakeholders alike.
Gathering Feedback from Users
Gathering feedback from users is a critical step in the prototyping and wireframing process for product managers. It is essential to involve users early on in the design phase to ensure that the final product meets their needs and expectations. By gathering feedback from users, product managers can identify any pain points or areas for improvement before investing significant time and resources into development.
One way to gather feedback from users is through usability testing. Usability testing involves observing users as they interact with a prototype or wireframe and gathering their feedback on its functionality and usability. Product managers can use this feedback to make informed decisions about the design and functionality of the product, ensuring that it meets the needs of its intended users.
Another method for gathering feedback from users is through surveys and questionnaires. These tools can be used to gather quantitative data on user preferences, opinions, and behaviors. Product managers can use this data to identify trends and patterns in user feedback, allowing them to make data-driven decisions about the design and functionality of the product.
In addition to usability testing and surveys, product managers can also gather feedback from users through focus groups and interviews. These methods allow product managers to engage directly with users, gaining valuable insights into their needs, preferences, and pain points. By listening to the feedback of users, product managers can ensure that the final product is user-centered and meets the needs of its target audience.
Overall, gathering feedback from users is a crucial step in the prototyping and wireframing process for product managers. By involving users early on in the design phase and listening to their feedback, product managers can ensure that the final product meets the needs and expectations of its intended users. Through usability testing, surveys, focus groups, and interviews, product managers can gather valuable insights that will inform their decision-making and ultimately lead to the development of a successful product.
Streamlining the Development Process
Streamlining the development process is crucial for product managers working in the prototyping and wireframing space. By implementing efficient strategies, product managers can ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget, while also meeting the needs and expectations of stakeholders. In this subchapter, we will explore some key techniques and best practices for streamlining the development process to help product managers achieve success in their roles.
One of the first steps in streamlining the development process is to establish clear goals and objectives for the project. Product managers should work closely with stakeholders to define the scope of the project, identify key deliverables, and establish a timeline for completion. By setting clear expectations from the outset, product managers can ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards a common goal.
Another important aspect of streamlining the development process is to prioritize tasks and allocate resources effectively. Product managers should work with their teams to identify the most critical tasks that need to be completed first and allocate resources accordingly. By focusing on high-priority tasks, product managers can ensure that the most important work gets done first, reducing the risk of delays and bottlenecks in the development process.
In addition to prioritizing tasks, product managers should also look for opportunities to automate and streamline repetitive tasks. By implementing tools and technologies that can automate manual processes, product managers can save time and resources, freeing up team members to focus on more strategic tasks. Automating tasks can also help reduce the risk of human error, ensuring that projects are completed accurately and efficiently.
Finally, communication is key to streamlining the development process. Product managers should maintain open lines of communication with stakeholders, team members, and other key players throughout the project. By keeping everyone informed of progress, changes, and challenges, product managers can ensure that everyone is working towards the same goals and can quickly address any issues that arise. Effective communication can help prevent misunderstandings, reduce delays, and keep projects on track for successful completion. By following these strategies and best practices for streamlining the development process, product managers can increase efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver high-quality products that meet the needs and expectations of stakeholders.
6: Case Studies in Prototyping and Wireframing
Case Study 1: Redesigning a Mobile App Interface
In this case study, we will explore the process of redesigning a mobile app interface to improve user experience and increase engagement. As a product manager, it is crucial to understand the importance of prototyping and wireframing in the design process. By using these tools effectively, you can visualize the changes you want to make to the interface and gather valuable feedback from stakeholders and users.
The first step in redesigning a mobile app interface is to conduct a thorough analysis of the current design. This includes identifying pain points, areas for improvement, and user feedback. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of the existing interface, you can make informed decisions about how to proceed with the redesign. This analysis phase is essential for setting clear goals and objectives for the redesign project.
Once you have completed the analysis phase, the next step is to create wireframes that illustrate the proposed changes to the interface. Wireframes are simple, low-fidelity representations of the interface that focus on layout, structure, and functionality. By creating wireframes, you can quickly iterate on different design ideas and gather feedback from stakeholders before investing time and resources in full-scale design.
After finalizing the wireframes, the next step is to create a high-fidelity prototype of the redesigned interface. High-fidelity prototypes are interactive representations of the interface that closely resemble the final product. By creating a high-fidelity prototype, you can test the functionality, usability, and aesthetics of the design before moving forward with development. This step is crucial for identifying any potential issues or challenges early in the design process.
In conclusion, redesigning a mobile app interface requires a systematic approach that includes analysis, wireframing, and prototyping. By using these tools effectively, product managers can ensure that the redesigned interface meets the needs and expectations of users. By investing time and resources in the design process, you can create a mobile app interface that is intuitive, engaging, and user-friendly.
Case Study 2: Prototyping a New Website Feature
In this case study, we will explore the process of prototyping a new website feature for a fictional e-commerce platform called “ShopEZ.” As a Product Manager, you will learn valuable insights into the prototyping and wireframing techniques used to bring new ideas to life in a user-friendly and efficient manner.
The first step in prototyping a new website feature is to clearly define the problem you are trying to solve. In the case of ShopEZ, the team identified a need for a more intuitive search function that would allow users to easily filter products by price, brand, and other relevant criteria. This feature would enhance the overall user experience and increase conversion rates on the platform.
Next, the team conducted user research to gather feedback on the current search function and identify pain points experienced by users. Through surveys, interviews, and usability testing, the team gained valuable insights into user preferences and behaviors. This information was used to inform the design of the new search feature prototype.
Using wireframing tools such as Sketch or Adobe XD, the team created low-fidelity prototypes of the new search feature. These wireframes allowed the team to quickly iterate on different design concepts and gather feedback from stakeholders. By incorporating feedback from users and internal team members, the team was able to refine the design and move forward with creating a high-fidelity prototype.
The high-fidelity prototype was then tested with a select group of users to gather feedback on the functionality and usability of the new search feature. Through A/B testing and user feedback sessions, the team was able to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to the design. This iterative process ultimately led to a successful launch of the new search feature on the ShopEZ platform, resulting in increased user engagement and satisfaction.
In conclusion, prototyping and wireframing are essential tools for Product Managers looking to innovate and improve the user experience of their products. By following a structured approach to prototyping, teams can quickly bring new ideas to life, gather feedback from users, and make data-driven decisions that lead to successful product launches.
Case Study 3: Wireframing a Dashboard for Data Visualization
In Case Study 3 of our book, we delve into the process of wireframing a dashboard for data visualization. As a Product Manager, understanding the importance of clear and effective data presentation is crucial in today’s digital landscape. Wireframing serves as a powerful tool in visualizing and refining the layout and design of a dashboard before moving on to the development stage.
The first step in wireframing a dashboard for data visualization is to identify the key metrics and data points that need to be displayed. This involves working closely with stakeholders, data analysts, and designers to understand the goals and objectives of the dashboard. By defining the purpose of the dashboard and the target audience, Product Managers can ensure that the wireframe accurately represents the information that needs to be communicated.
Once the key metrics and data points have been identified, the next step is to create a rough sketch or wireframe of the dashboard layout. This initial wireframe serves as a blueprint for the design team to work from, providing a visual representation of the structure and hierarchy of the data. Product Managers should collaborate with designers to iterate on the wireframe, making adjustments and refinements based on feedback from stakeholders and usability testing.
After finalizing the wireframe, the next step is to add in the visual elements and interactive features that will bring the dashboard to life. This includes selecting colors, fonts, icons, and other design elements that enhance the readability and usability of the data visualization. Product Managers should work closely with designers to ensure that the visual design aligns with the overall brand guidelines and user experience objectives.
In conclusion, wireframing a dashboard for data visualization is a critical step in the product development process. By carefully planning and designing the layout and structure of the dashboard, Product Managers can ensure that the data is presented in a clear and impactful way. Through collaboration with stakeholders, designers, and data analysts, Product Managers can create wireframes that effectively communicate key metrics and data points, setting the stage for a successful product launch.
7: Future Trends in Prototyping and Wireframing
Virtual Reality Prototyping
Virtual reality prototyping is a cutting-edge tool that product managers can use to create immersive and interactive prototypes of their products. By simulating a realistic environment, virtual reality prototyping allows product managers to test user interactions in a more engaging way than traditional wireframing methods. This technology is especially useful for products that involve 3D elements or spatial interactions, such as video games, virtual tours, or augmented reality applications.
One of the key benefits of virtual reality prototyping is the ability to gather valuable feedback from users early in the design process. By allowing users to interact with a virtual prototype, product managers can identify potential usability issues and make necessary adjustments before investing in the development of the final product. This iterative approach can save time and resources in the long run, as it minimizes the risk of costly redesigns or rework later on.
In addition to user testing, virtual reality prototyping can also be used to showcase a product concept to stakeholders or investors. By presenting a realistic and immersive experience, product managers can effectively communicate their vision and generate buy-in from key decision-makers. This can be especially useful for products that are difficult to visualize or explain through traditional methods, such as complex spatial designs or interactive experiences.
When it comes to creating virtual reality prototypes, product managers have a variety of tools and platforms to choose from. Some popular options include Unity, Unreal Engine, and Sketchfab, which offer a range of features for designing, testing, and sharing virtual prototypes. Product managers should carefully consider their project requirements and budget constraints when selecting a virtual reality prototyping tool, as each platform has its own strengths and limitations.
Overall, virtual reality prototyping is a powerful tool that can help product managers bring their ideas to life and gather valuable feedback from users and stakeholders. By leveraging this technology, product managers can create more engaging and interactive prototypes that accurately represent the final product, ultimately leading to a more successful product launch. As virtual reality continues to evolve and become more accessible, product managers in the prototyping and wireframing niche should consider incorporating this tool into their toolkit to stay ahead of the competition and deliver innovative products to market.
Artificial Intelligence in Wireframing
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized the way we approach wireframing in product development. In this subchapter, we will explore the role of AI in wireframing and how it can benefit product managers in creating more efficient and effective prototypes.
One of the key advantages of using AI in wireframing is its ability to analyze large amounts of data quickly and accurately. By utilizing machine learning algorithms, AI can identify patterns and trends in user behavior, allowing product managers to make informed decisions about the design of their prototypes. This data-driven approach can lead to more user-centric designs that are tailored to the needs and preferences of target users.
Another benefit of AI in wireframing is its ability to automate repetitive tasks, such as creating wireframes based on predefined templates or design guidelines. This can save product managers valuable time and resources, allowing them to focus on more strategic aspects of product development. Additionally, AI can help streamline the collaboration process by providing real-time feedback and suggestions to team members working on wireframes.
AI can also assist product managers in conducting A/B testing and gathering insights from user feedback. By analyzing user interactions with wireframes, AI can help identify areas for improvement and suggest alternative design solutions. This iterative process can lead to faster iterations and more successful prototypes that better meet user needs and expectations.
Overall, incorporating AI into wireframing can enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness of the prototyping process for product managers. By leveraging the power of AI, product managers can create more innovative and user-friendly prototypes that drive product success. As AI continues to advance, it will be increasingly important for product managers in the prototyping and wireframing niches to embrace this technology and leverage its capabilities to stay ahead of the competition.
Collaborative Prototyping Tools
In today’s fast-paced world of product development, collaboration is key. As a Product Manager, you understand the importance of working together with your team to create innovative and user-friendly products. Collaborative prototyping tools are essential for streamlining the design process and ensuring that everyone is on the same page. In this subchapter, we will explore some of the top collaborative prototyping tools available to help you and your team create amazing products.
One of the most popular collaborative prototyping tools on the market is Figma. Figma allows multiple team members to work on a design in real-time, making it easy to collaborate and iterate quickly. With features like commenting and version control, Figma is a must-have tool for any Product Manager looking to streamline their prototyping process.
Another great option for collaborative prototyping is InVision. InVision allows teams to create interactive prototypes that can be shared and tested with stakeholders. With features like live collaboration and real-time feedback, InVision is a powerful tool for Product Managers looking to improve their prototyping process.
For teams that work in Sketch, Abstract is a great tool for collaborative prototyping. Abstract allows team members to work on design files together, ensuring that everyone is working with the most up-to-date version of the file. With features like branching and merging, Abstract is a valuable tool for Product Managers working with complex design files.
No discussion of collaborative prototyping tools would be complete without mentioning Adobe XD. Adobe XD allows teams to create interactive prototypes that can be shared and tested with stakeholders. With features like design systems and shared components, Adobe XD is a powerful tool for Product Managers looking to create consistent and user-friendly designs.
In conclusion, collaborative prototyping tools are essential for Product Managers looking to streamline their design process and create amazing products. Whether you choose Figma, InVision, Abstract, or Adobe XD, incorporating a collaborative prototyping tool into your workflow will help you and your team work more efficiently and effectively. By leveraging the power of these tools, you can create innovative and user-friendly products that will delight your customers.
Recap of Key Concepts
In this subchapter, we will recap some of the key concepts that we have covered in this book so far. As a product manager in the field of prototyping and wireframing, it is crucial to have a strong understanding of these concepts in order to effectively create and communicate your product vision.
First and foremost, prototyping is a crucial step in the product development process. It allows you to quickly and effectively test out different ideas and concepts before investing significant time and resources into full-scale development. By creating prototypes, you can gather valuable feedback from stakeholders and users, which can help you refine your product and make informed decisions moving forward.
Wireframing, on the other hand, is a more detailed and structured form of prototyping. It involves creating a visual blueprint of your product, outlining the layout, navigation, and functionality of each screen or page. Wireframes are essential for ensuring that all stakeholders have a clear understanding of the product’s design and functionality before moving into development.
Another key concept we have discussed is the importance of iteration in the prototyping and wireframing process. It is rare for a product to be perfect on the first try, which is why it is essential to iterate on your designs based on feedback and testing. By continually refining and improving your prototypes, you can ensure that your final product meets the needs and expectations of your users.
Lastly, we have emphasized the importance of collaboration in the prototyping and wireframing process. As a product manager, it is crucial to work closely with designers, developers, and other stakeholders to ensure that everyone is aligned on the product vision and goals. By fostering a collaborative and inclusive environment, you can leverage the diverse expertise of your team to create a successful and impactful product.
In conclusion, prototyping and wireframing are essential tools for product managers in the modern tech industry. By understanding and applying the key concepts we have covered in this book, you can streamline your product development process, gather valuable feedback, and ultimately create innovative and user-friendly products that meet the needs of your target audience.
Final Thoughts on Prototyping and Wireframing in Product Management
In conclusion, prototyping and wireframing are essential tools in the product manager’s toolkit. These techniques allow product managers to visualize their ideas, gather feedback from stakeholders, and iterate on their designs quickly. By creating prototypes and wireframes, product managers can test out different concepts and make informed decisions about the direction of their products.
One key takeaway from this subchapter is the importance of involving stakeholders early and often in the prototyping and wireframing process. By getting feedback from users, developers, designers, and other key stakeholders, product managers can ensure that their designs meet the needs of all parties involved. This collaborative approach can lead to better products that are more likely to succeed in the market.
Another important consideration is the need to balance speed and quality when prototyping and wireframing. While it’s important to iterate quickly and get feedback as soon as possible, product managers must also ensure that their prototypes are high-quality and accurately represent the final product. Finding the right balance between speed and quality is key to successful prototyping and wireframing.
Overall, prototyping and wireframing are valuable tools for product managers looking to create successful products. By incorporating these techniques into their workflow, product managers can streamline the design process, gather valuable feedback, and make informed decisions about their products. With the right approach and mindset, prototyping and wireframing can help product managers bring their ideas to life and create products that truly resonate with their target audience.